Keppel’s Column in Thorp Hesley, overlooking Wentworth Woodhouse, near Rotherham in South Yorkshire, was commissioned in 1773 by Charles Watson Wentworth, 2nd Marquess of Rockingham. The parkland of Wentworth Woodhouse and the surrounding area contain a number of follies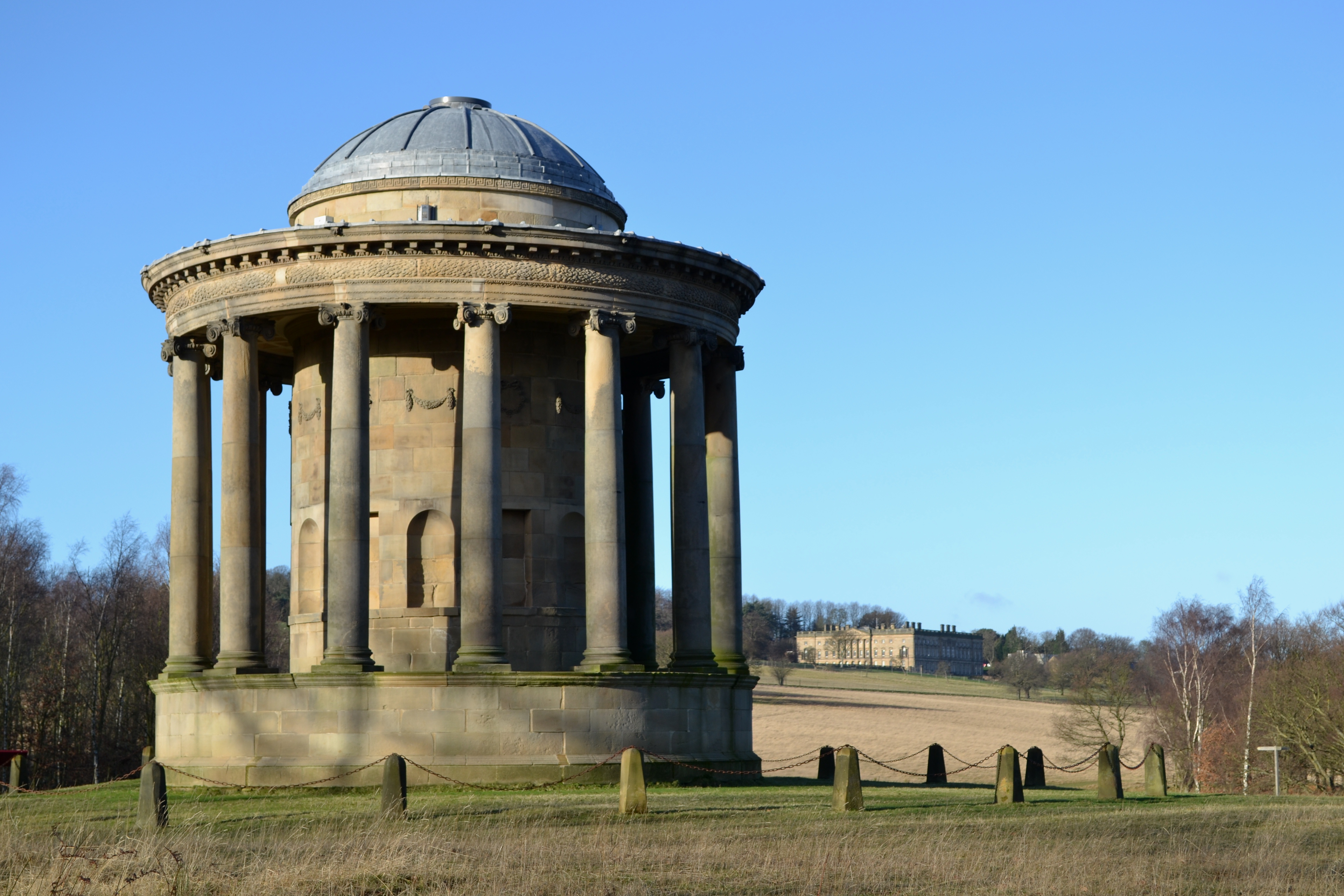
Ornamental structure with no practical purpose, built to enhance a designed garden or landscape., including Hoober StandMonumental tower in the form of a tapering pyramid topped with a hexagonal lantern, named for the ancient wood in which it was erected., the Needle’s Eye, the Rockingham MausoleumMonument commissioned by the Earl Fitzwilliam as a memorial to the second Marquess of Rockingham in 1783., the Doric Temple and the Bear Pit.
Keppel’s Column, an eye-catcher, was originally intended to be a pedestal surmounted by obelisk, but the design was repeatedly altered; the final version by Yorkshire architect, John CarrProlific architect who worked mainly in the North of England, (1723–1807)., is a 35-metre (115 ft) tall Tuscan column topped by a viewing platform. The column was finished in 1780 after the earl’s friend, Admiral Augustus Keppel, was acquitted following his court-martial after failing to engage the French at the Battle of Ushant in 1778.[1]
Structure
The massive Tuscan column is built of dressed stone and stands on an ashlarMasonry of squared and finely cut or worked stone, commonly used for the facing of a building. sandstone plinth. It is about 35 metres (115 ft) in height topped with a large abacus,[a]Flat slab forming the top of a capital on a column which forms its rectangular viewing platform. The viewing platform has a metal balustrade. A doorway in the east side of the plinth has been concreted over. Five round-headed windows are set in a vertical line on three sides of shaft and six windows are on the side opposite the door but most of the lower windows have been blocked up. The column was not completed to its intended height, which accounts for the modification of entasis[b]A slight convex curve in the column to correct the optical illusion of concavity or hollowness produced by a straight shaft towards the top.[1]
Condition
The column was designated a Grade II* listed structure in 1986, but its condition has since deteriorated, with erosion to the stonework and significant structural cracks. Emergency repairs ware made to the stairwell and viewing platform.[2] In 2021 with funding from Rotherham Council, the Heritage Stimulus Fund and the Wentworth Amenity Trust restoration of the monument began.[3] The column is being restored and access to the top of the landmark will once again be possible.[2]