Wikimedia Commons
Turlington’s Balsam of Life was a patent medicine developed by the English merchant Robert Turlington. He succeeded in obtaining a royal patentOfficial letters or instructions issued by or on behalf of the Crown. from King George II in 1744, which gave him the right to pursue anyone attempting to pass off their own product as his,[1] one of the earliest medicinal patents.[2][a]The earliest medicinal patent was granted in 1698, for Epsom Salts.[3] In his patent application Turlington claimed that his balsam contained 27 ingredients, and was effective in the treatment of “kidney and bladder stones, cholic, and inward weakness”, a list of ailments he greatly expanded upon in a 46-page brochure printed shortly afterwards.[4] Turlington’s Balsam quickly became popular in England and the American colonies.[1]
Packaging
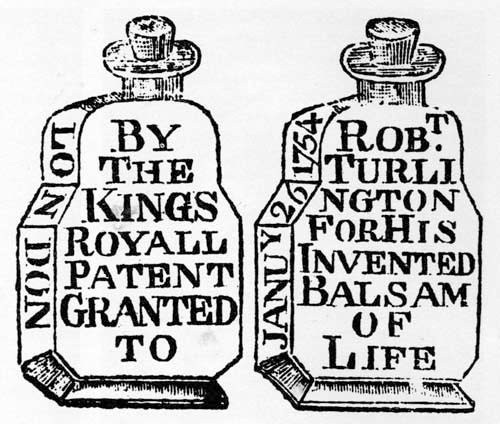
During the 17th and 18th centuries the manufacturers of patent medicines began to use packaging as a tool to differentiate their products from those of their competitors, as there was often little to visually distinguish between the medications themselves.[b]Patents only applied to the medication, not to its packaging, therefore competitors were free to copy a medication’s packaging in an effort to increase their sales at the expense of the patented product.[5] In Turlington’s case that resulted in his changing the shape of the bottle containing his balsam at least four times in the ten years following the granting of his patent, culminating in an elaborately embossed tablet-shaped bottle introduced in 1754.