Back-to-backs are a form of terraced houses in the United Kingdom, built from the late 18th century through to the early 20th century in various guises. Many thousands of these dwellings were built during the Industrial Revolution for the rapidly increasing population of expanding factory towns. Back-to-backs share party walls on three of their four sides, with the front wall having the only door and windows.
As back-to-backs were built as the cheapest possible housing for the impoverished working class, their construction was usually sub-standard. Their configuration did not allow for sufficient ventilation or sanitation. Toilets and water supplies were shared with multiple households in enclosed courtyards. Back-to-backs gained an unsavoury reputation for poor levels of health and hygiene.
Around the mid-19th century, this form of housing was deemed unsatisfactory and a hazard to health. The passage of the Public Health Act 1875 permitted municipal corporations to ban new back-to-backs, replaced in the next phase of building by byelaw terraced houses. Leeds City Council opted not to enforce the ban however; the popularity of back-to-back houses with builders and residents led to their continued construction in Leeds until the 1930s.
Most back-to-backs were demolished in waves of slum clearances, although many remain in Leeds and Bradford. Birmingham and Liverpool, where many thousands of these homes were built, each chose to retain a single example as a tourist attraction. The Birmingham Back to Backs is now operated as a historic house museum by the National Trust; other museum examples of back-to-back houses are managed by the Museum of Liverpool and Bradford Industrial Museum.
Description
Wikimedia Commons
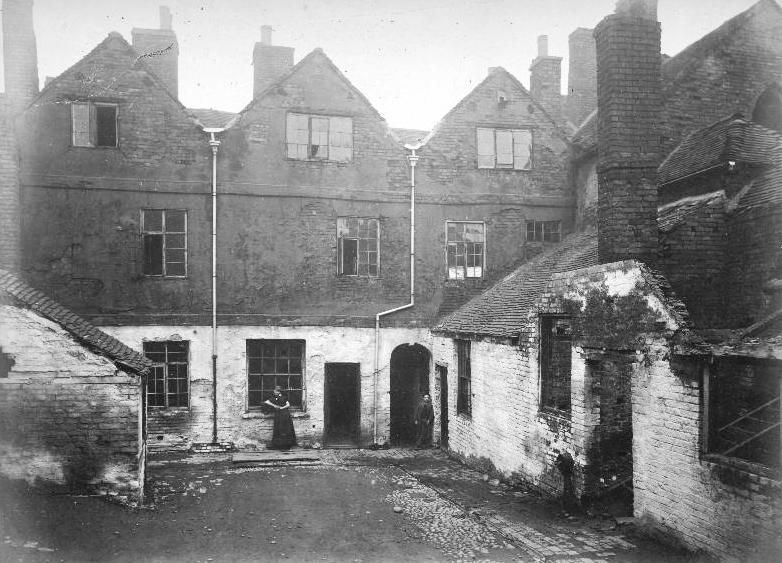
Low quality houses were constructed for working class people at a high density, with scant regard for space, comfort or quality of life. Most back-to-backs were small: early examples had just a single room on each floor, while later houses were two-up two-down. Every house shared a rear wall, whether with a house directly behind or with an industrial building. Given that the house usually shared three of its four walls with neighbouring buildings, back-to-back houses were notoriously ill-lit and poorly ventilated.[1] Such was the initial lack of consideration for hygiene, that some houses were found to have been built over open drains covered only by boards.[2]
The term “back-to-back” should not be confused with “through” terraced houses, the backs of which face each other across an alleyway, and are thus not contiguous like a true back-to-back. Back-to-back houses can also be known as blind-backs,[3] particularly when built up against factory walls, or occasionally as a terrace of houses standing on its own.
History
Early houses
The population of the city of Leeds was around 30,000 by 1800, which later doubled and then tripled, creating a problem of insufficient housing. The first back-to-back houses were built by 1790 in Briggate, Leeds, by opportunists who realised that the structural setup allowed for a cost saving by not requiring roads or drainage,[4] with population density housing up to 300 people in 60–75 properties per acre. There was no universally accepted blueprint for how the houses should be constructed; the worst (and often earliest) had a single room on each floor and no damp proofing. Sanitation comprised earth toilets in whatever available space existed, which may have been underneath bedrooms, and a public water supply from intermittent standpipes.[5] Initially, houses were built around a communal courtyard, but later they were built onto streets.[6] Houses of this type had become common in inner city areas of Victorian England, especially in Birmingham, Bradford,[7] Leeds, Liverpool, Manchester, Salford and in Nottingham, where about 7500 of their 11,000 houses (approximately 68 per cent)[2] were built back-to-back. Town authorities were well aware that back-to-backs were undesirable, but seemed unable to prevent their construction. The Building and Improvement Committee reported to Bradford Council that more than three-quarters of new dwellings were “laid out upon that objectionable principle”.[7] The passage of the Artisans’ and Labourers’ Dwellings Improvement Act 1875 gave councils permission to compulsory purchase slum housing, but few took advantage of the opportunity.[8]
During the 18th and 19th centuries, owners of mills and mines built significant numbers of back-to-backs to maximize the number of workers that could live in the least amount of space, while keeping costs low. Advocates of the design suggested that they were easier to keep warm owing to their single outside wall, but the absence of rear yards meant there was no space for exterior toilets, only communal ones that spread diseases rapidly.[9] In the oldest parts of Birmingham, early back-to-back houses were associated with filth, poor ventilation and pools of stagnant water, despite being home to the greatest number of working-class people within the city.[2]
19th century
Rapid urbanisation led to fields and allotments disappearing in favour of cheaply built houses, often tightly packed together into the smallest space available. Houses were built on top of inadequate foundations and with substandard materials to reduce costs. Each house was separated by a single brick depth with a small room on each floor; ground-floor rooms served multiple purposes, as the remaining available space was used for bedrooms.[10] By the 1830s, back-to-back houses had gained a reputation nationwide for spreading disease, and major cities including Manchester and Liverpool prohibited their construction in the 1840s and 1860s respectively. The Leeds Improvement Act of 1866 imposed regulations on the building of new houses, which included gated yards, wider streets and improved interior design. The Medical Officer for Health unsuccessfully sought to abolish their construction in about 1880,[5] by which time population density had improved to 200 people living in 50–60 houses per acre.[11]
Significant change came with the introduction of the byelaw terraced house to comply with the Public Health Act 1875. Further improvements were introduced in 1890, such as the inclusion of a basement or ground-floor kitchen, a small garden and a private toilet for each household.[11] Subsequent acts including the Housing of the Working Classes Act 1885 and the Housing of the Working Classes Act 1890 imposed additional construction requirements.
Leeds appears to have been a special case. Figures from 1899 suggest that 72 per cent of all houses constructed annually in that city were back-to-back, identical to 15 years earlier, a percentage that did not decrease until 1914. Small families with children in the city had little choice but to live in back-to-back houses, as they dominated the affordable market.[12] It was anticipated that the byelaw terraced house regulation would prevent the construction of back-to-back houses, yet Leeds Council initially opted not to enforce it, particularly where building contractors unmotivated by social or aesthetic considerations could influence decisions to ensure their own contracts and interests were put ahead of build quality. Consequently, the density of housing in some areas, as well as its manner of construction, had adverse effects on sale and rental prices, particularly as other towns offered houses with greater space and improved sanitation; a new property built in Sunderland would have been provided with its own water closet, while a new property in Leeds may have had one shared, up until 1912.[13]
Pre-First World War

Wikimedia Commons
By the turn of the 20th century, back-to-back houses had become unpopular with residents and the government, who sought to ban their construction and eradicate existing properties nationwide. Among the primary concerns cited were health and ventilation, as statistics were revealing that residents of back-to-back houses suffered from relatively poor health. In Manchester, Dr James Niven noted that mortality rates among those living in back-to-back houses exceeded those from through-houses by 40 per cent, along with an increased incidence of infectious diseases and diarrhoea. A change in the law in 1909 forbade the erection of this style of house.[14]
Between the wars
The advent of council housing after the First World War resulted in councils organising programmes of statutory slum clearances as part of post-war housing redevelopment programmes. Such initiatives gathered pace in the 1920s, with the beginning of mass demolition of back-to-back houses and the construction of “homes fit for heroes”.[15]
By the early part of the 20th century the local council in Leeds had spent about £1 million in acquiring older, inadequate back-to-back houses for demolition.[14] But it continued to build similar houses until 1937, despite that style of construction having been outlawed in 1909,[9] when it was decided that houses should be of an overall higher quality.[16] By 1926 Leeds had 72,000 back-to-backs, of which 32,000 were described by Dr Christoper Addison as being “abominations”, having been condemned as unfit for many years by that time, despite still being lived in;[17] only 12,000 (less than 17 per cent) were given a moderate health pass by Neville Chamberlain’s[18] Unhealthy Areas Committee.[19] Other cities had smaller numbers, such as Bradford (33,000) and Nottingham (5000) respectively.[20] MP Sir John Birchall described Leeds in 1930 as having “an unenviable notoriety for its back-to-back houses”, although popularity among residents had increased. He unsuccessfully proposed in 1930 to permit the construction of back-to-back houses in blocks of four, given that back-to-backs were generally cheaper to build than standard through houses and that having two external walls per property would alleviate the ventilation concerns that plagued earlier residences.[21]
Post-Second World War
Following the Second World War and the Blitz aerial bombing of industrial cities, Britain was ready for a new wave of slum demolition and construction of more suitable housing. For example, Birmingham had about 40,000 back-to-backs in 1931[22] but only 29,182 by September 1946.[23]
In Leeds around 1953, there were 30,000 people waiting for council housing, of which 16,000 comprised back-to-back housing built before 1844 that were pending clearance as slum housing.[24] The quality until 1844 had been sub-standard, yet 16,000 of those properties were still inhabited in 1951, along with a further 28,000 slightly better houses constructed between 1844 and 1874. The pre-1844 houses were by that time in a state of disrepair, and overcrowding was a concern, particularly when families were occupying what was originally intended for single or dual occupancy.[25]
By 1959 Leeds and Birmingham each had 60,000 back-to-back houses, and Members of Parliament were calling for the demolition to be accelerated. William Wheeldon, a Labour and Co-operative MP, pointed out that “the most distressing thing” was that little had changed in generations:[26]
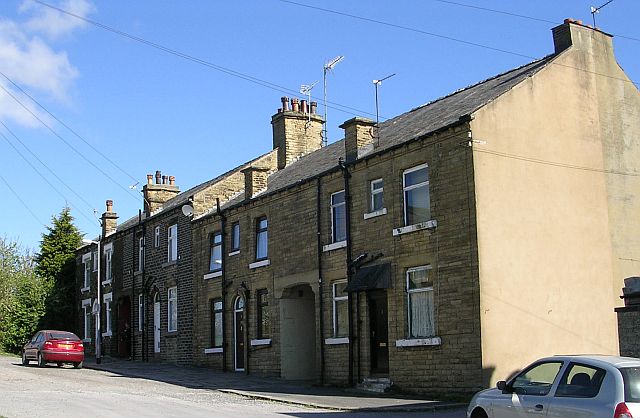
Contemporary usage

Wikimedia Commons
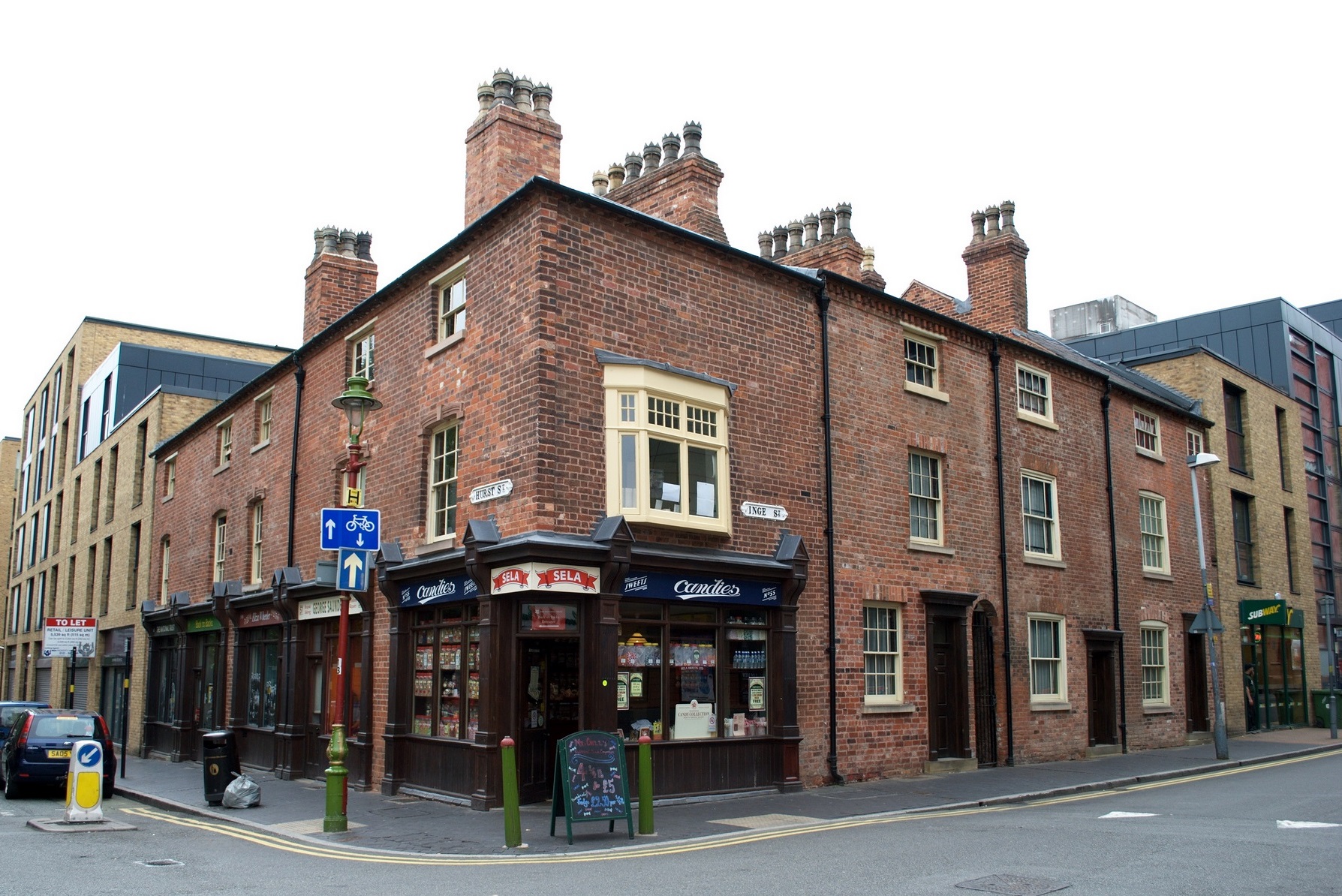
Leeds and its surrounding region is the only area where back-to-back houses still exist in large numbers, having been refurbished to include “mod cons” such as indoor bathrooms and central heating. These modernised back-to-backs are popular with residents because they are easier to maintain than typical houses. The houses have proved to be popular with buy to let investors, who helped to increase prices significantly during the early mid-2000s. The house style is also popular among student populations, as little exterior maintenance is required and they are often close to universities and colleges, particularly in the areas of Headingly, Burley and Kirkstall.[9]
Although banned by existing building regulations for new builds, architects are keen for the regulations to be relaxed, particularly as many of the historical health concerns associated with back to-back-housing, such as open sewers and communal toilets, are no longer relevant.[9]
A study was conducted in 2008 to canvass the views of the communities living in these properties, to help ensure that they could continue in use into the 21st century. Seventy-five per cent of those questioned suggested that the heritage value of the houses was important to the identity of Leeds. Overall, 51 per cent of respondents were positive, and 45 per cent felt negatively towards them. Residents of these back-to-backs generally felt strongly about their heritage value, but their opinions were not valued as highly as non-residents or professionals. Despite the feedback, there was insufficient recognition that the properties should be protected because of their perceived heritage value.[27]
Preservation as museums
The Birmingham Back to Backs are a historic house museum created by The National Trust for the city’s last remaining back-to-back houses. The dwellings are furnished as they would have been in the 19th century and are now Grade II listed buildings.[28] According to the BBC, this is the last example of such housing grouped around a court.[1]
In Liverpool, back-to-back court housing was once home to more than 40 per cent of its population,[29] before demolition during the 1960s and 1970s as part of slum house clearance programs. A set of nine pairs of these houses survived and were restored as part of a museum attraction.[30] A proposal to preserve and restore the city’s last surviving court housing block was made in 2016, with structural work taking place to secure the building, as well as a new roof to prevent further water damage. The project would complement the existing court dwellings at the Museum of Liverpool, which opened in 2011 and recreates a former street from 1870 in the area around Scotland Road.[29]
The Bradford Industrial Museum has a block of back-to-backs decorated as dwellings of 1875, the Second World War, and the 1970s.[31]
This article may contain text from Wikipedia, released under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.