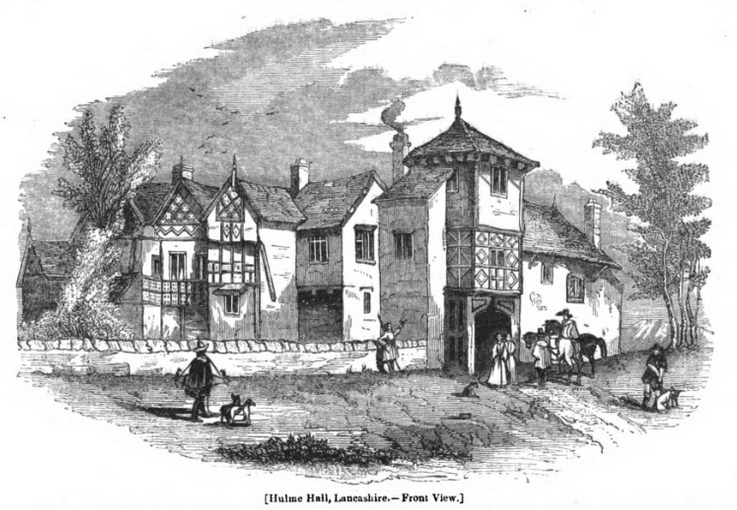
Some suggestions for "Greater Manchester Treasure", listed by relevance (177)
Bradford CollieryBradford Colliery was a coal mine in Bradford, Manchester, England.
Bradford Colliery BrickworksBradford Colliery Brickworks operated on the site of the Bradford Colliery in Bradford, Greater Manchester, then in the historic county of Lancashire, England,
DamhouseGrade II* listed building in Tyldesley but considered to be in Astley, Greater Manchester, England. It has served as a manor house, sanatorium, and, since restoration in 2000, houses offices, a clinic and tearooms.
Yew Tree CollieryFormer coal mine operating on the Manchester Coalfield after 1845 in Tyldesley, which was then in the historic county of Lancashire, England.
Astley and Tyldesley CollieriesColliery company formed in 1900, became part of Manchester Collieries in 1929, and some of its collieries were nationalised in 1947.
Great Haigh SoughTunnel or adit driven under Sir Roger Bradshaigh’s Haigh Hall estate between 1653 and 1670, to drain his coal and cannel pits.
Barnfield MillsFormer complex of six cotton spinning mills, known locally as Caleb Wright's, on either side of Union Street in Tyldesley.
Garrett HallFormer manor house and now a Grade II listed farmhouse in Tyldesley, Greater Manchester, England.
Astley and Bedford MossesAreas of peat bog south of the Bridgewater Canal and north of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway in Astley and Bedford, Leigh, England.
Boothstown Mines Rescue StationMines rescue station serving the collieries of the Lancashire and Cheshire Coal Owners on the Lancashire Coalfield, opened in 1933.
Manchester Free LibraryFirst library to be set up under the provisions of the Public Libraries Act 1850, in Manchester, England, which allowed local authorities to impose a local tax of one penny to pay for the service.
Barrow BridgeModel village started by John and Robert Lord, who built a cotton mill next to the Dean Brook in the north-west outskirts of Bolton in Greater Manchester, England.
Manchester Zoological GardensGardens opened in 1838, on a 15-acre (6 ha) site between Broom Lane and Northumberland Street in Broughton, now in Salford, England.
Haigh HallHistoric country house in Haigh, near Wigan in Greater Manchester England.
Leigh Town HallLeigh Town Hall stands facing the parish church across the Civic Square at its junction with Market Street in Leigh, Greater Manchester, England. It was designed for the Municipal Borough of Leigh by James Caldwell Prestwich, who had an architectural practice in the town.
Magee Marshall & CompanyBrewer which operated from the Crown Brewery in Bolton, Lancashire, England from 1888 until being taken over by Greenall Whitley in 1958.
Howe Bridge Mines Rescue StationFirst mines rescue station on the Lancashire Coalfield, opened in 1908 in Lovers Lane Howe Bridge, Atherton, Lancashire, England.
Leigh SpinnersLeigh Spinners or Leigh Mill is a Grade II* listed double cotton spinning mill near the Bridgewater Canal in Bedford, Leigh, England.
Belle Vue Zoological GardensLarge zoo, amusement park, exhibition hall complex and speedway stadium in Belle Vue, Manchester, England, opened in 1836.
Sharston HallFormer manor house built in Sharston, an area of Wythenshawe, Manchester, England in 1701.
Kenyon and Leigh Junction Railway
The Kenyon and Leigh Junction Railway (K&LJR) opened on 3 January 1831 linking the Bolton and Leigh Railway (B&LR), which terminated near the Leigh Branch of the Leeds and Liverpool Canal, to the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR) at Kenyon.
Tyldesley Little TheatreSmall "back street" theatre in Lemon Street, Tyldesley, Greater Manchester, England.
Morleys HallMorleys Hall, a moated hall converted into two houses on the edge of Astley Moss in Astley, Greater Manchester, England, was largely rebuilt in the 19th century on the site of a medieval timber house.
Free Trade HallPublic hall constructed in 1853–1856 on St Peter's Fields, the site of the Peterloo Massacre, now a Radisson hotel.
Manchester BlitzHeavy bombing of the city of Manchester and its surrounding areas in North West England during the Second World War by the Nazi German Luftwaffe.
Capitol Theatre, ManchesterFormer cinema in Didsbury, Manchester, used as television studios by ITV contractor ABC from 1956 to 1968.
Worthington Hall, WiganWorthington Hall is an Elizabethan farm house on Chorley Lane in Wigan, Manchester, England. An inscription on a lintel in the gabled porch dates the building to 1577.
Gin Pit CollieryColliery that operated on the Lancashire Coalfield from the 1840s in Tyldesley Lancashire, England.
St George’s Colliery
St George's Colliery, known locally as Back o't' Church, was a coal mine on the Manchester Coalfield that was sunk in 1866 in Tyldesley, Lancashire, England.
Nook CollieryCoal mine on the Manchester Coalfield after 1866 in Tyldesley, Lancashire, England.
New Hall moatScheduled monument in Tyldesley, Greater Manchester, England, which comprises a moat and an island platform on which a modern house has been built.
Atherton HallCountry house and estate in Atherton in Lancashire, England built between 1723 and 1742, demolished in 1824.
Manchester Royal ExchangeFormer cotton exchange damaged by two bombs, now comprising a theatre and shopping centre.
Longford CinemaCinema opposite Stretford Mall on the eastern side of the A56 Chester Road, perhaps the most visually striking building in the town.
Hanging BridgeMedieval structure spanning the Hanging Ditch, which connected the rivers Irk and Irwell in Manchester, England, part of the city's medieval defences.
Wallsuches BleachworksBleachworks that takes its name from an area of Horwich in Greater Manchester, England. The area is notable for the bleachworks started by Thomas Ridgway.
Manchester MummyMummified body of Hannah Beswick (1688–1758, a wealthy woman with a pathological fear of premature burial.
Ramsden’s Shakerley CollieriesRamsden’s Shakerley Collieries was a coal mining company operating from the mid-19th century in Shakerley, Tyldesley in Lancashire, England.
Timperley HallFormerly moated manor house in Timperley, Greater Manchester, England, first recorded in 1560, but almost certainly built to replace an earlier medieval structure.
Ancoats HallPost-medieval country house built in 1609 in Ancoats, Manchester by Oswald Mosley, a member of the family who were Lords of the Manor of Manchester.
The Walking Horse locomotiveLancashire’s first steam locomotive, built by Robert Daglish in 1812 at the Haigh Foundry for colliery owner, John Clarke; it entered service the following year.
Edward OrmerodEnglish mining engineer and inventor who worked at Gibfield Colliery in Atherton, Lancashire where he devised and tested his safety device, the Ormerod safety link or detaching hook.
Port of ManchesterCustoms port in North West England, created on 1 January 1894 and closed in 1982.
Great Boys CollieryGreat Boys Colliery in Tyldesley was a coal mine operating on the Manchester Coalfield in the second half of the 19th century in Lancashire, England.
Fairbottom Bobs
Fairbottom Bobs, an 18th-century Newcomen-type beam engine, was used to pump water from a coal pit near Ashton-under-Lyne, is probably the world’s second-oldest surviving steam engine.
Cleworth Hall Colliery
Cleworth Hall Colliery on the Lancashire Coalfield operated between 1880 and 1963 in Tyldesley, Lancashire, England.
Burning wellsPhenomenon known in the area around Wigan in Lancashire from at least the 17th century.
Fletcher, Burrows & CompanyOwner of collieries and cotton mills in Atherton in North West England.
Nico DitchLinear earthwork between Ashton-under-Lyne and Stretford in Greater Manchester, England.
Stretford Public HallPublic hall built in 1878 by the Manchester's first multi-millionaire John Rylands.
Ordsall HallLarge former manor house in the historic parish of Ordsall, Lancashire, England, now part of the City of Salford, in Greater Manchester.
Peelwood CollieryPeelwood Colliery on the Manchester Coalfield in Shakerley, Tyldesley, Lancashire, began producing coal in 1883.
Chat MossLarge area of peat bog that makes up 30 per cent of the City of Salford, in Greater Manchester, England
Combermere CollieryCombermere Colliery was sunk by the Tyldesley Coal Company on the Manchester Coalfield after 1867 in Shakerley, Tyldesley in Lancashire, England.
New Lester CollieryColliery on the Manchester Coalfield opened after 1872 by James and William Roscoe in Tyldesley, Lancashire, England.
Barton AqueductAqueduct, designed by James Brindley and opened on 17 July 1761, which carried the Bridgewater Canal over the River Irwell at Barton-upon-Irwell, in the historic county of Lancashire, England.
Barton Swing AqueductAqueduct in Barton upon Irwell, Greater Manchester, England carrying the Bridgewater Canal across the Manchester Ship Canal, opened in 1894.
Wythenshawe Hall16th-century medieval timber-framed historic house and former manor house in Wythenshawe, Manchester, England.
Trafford Town HallOfficially opened as Stretford Town Hall on the granting of Stretford's charter on 16 September 1933.
Smithills HallSmithills Hall in Bolton, Greater Manchester, is one of the oldest manor houses in the northwest of England, dating in parts from the 15th century.
Tyldesley LooplineRailway line built in 1864 to connect local collieries to the Liverpool–Manchester main line.
Trafford ParkFirst planned industrial estate in the world, and still the largest in Europe.
IrlamBuilt-up area in the City of Salford, Greater Manchester, England, lying on flat ground on the south side of the M62 motorway and the north bank of the Manchester Ship Canal.
Dunham CastleEarly medieval moated motte and bailey castle just to the northwest of present-day Dunham Massey Hall in Greater Manchester, England.
Ullerwood CastleEarly medieval fortification, possibly a shell keep, in Ringway, Greater Manchester, England.
Pennington FlashLake formed by mining subsidence in Leigh, Greater Manchester, the largest body of open water in Wigan.
Victoria ArchesSeries of bricked-up arches in an embankment of the River Irwell in Manchester. They served as business premises, landing stages for steam packet riverboats and as Second World War air-raid shelters.
Manchester CoalfieldPart of the Lancashire Coalfield. Some easily accessible seams were worked on a small scale from the Middle Ages, and extensively from the beginning of the Industrial Revolution until the last quarter of the 20th century.
Pendleton CollieryFormer colliery that operated on the Manchester Coalfield from the late 1820s. It was a major employer but was subject to water ingress, which ultimately bankrupted its owner.
Municipal Borough of StretfordCreated in 1894 and granted a charter of incorporation in 1933, becoming a municipal borough. Abolished in 1974, the area it controlled is now part of the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford in Greater Manchester.
Tyldesley Urban DistrictTyldesley cum Shakerley Urban District and its successor, Tyldesley Urban District. was from 1894 to 1974 a local government district in Lancashire, England. In 1974 the urban district was abolished and its former area was transfered to the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan in Greater Manchester.
Hulme Arch BridgeBridge in Hulme, Manchester, England, supporting Stretford Road as it passes over Princess Road, part of the regeneration of that area of Manchester.
Municipal Borough of LeighLocal government district in Lancashire, England, created in 1899 and abolished in 1974.
Atherton Urban DistrictAtherton Urban District was from 1894 to 1974 a local government district in Lancashire, England.
Carrington MossLarge area of peat bog near Carrington in Greater Manchester, England. Originally an area of grouse moorland, it was reclaimed in the latter half of the 19th century for farming and the disposal of Manchester's waste.
Dovestone ReservoirsDovestone and its associated reservoirs occupy the valleys of the Greenfield and Chew Brooks above the village of Greenfield, on Saddleworth Moor in Greater Manchester.
Hollingworth LakeHollingworth Lake was built as the main water source for the Rochdale Canal.
Wharton Hall CollieryWharton Hall Colliery was in Little Hulton on the Lancashire Coalfield in Lancashire, north west England.
Hulton CollieriesThe Hulton Colliery Company operated on the Lancashire Coalfield from the mid-19th century in Over Hulton and Westhoughton, Lancashire.
Blackstone EdgeGritstone escarpment in the South Pennines rising to 1,549 feet (472 m) above sea level
Mellor hill fortPrehistoric site dating from the British Iron Age, situated on a hill in the village of Mellor, Greater Manchester, on the western edge of the Peak District.
Andrew Knowles & SonsAndrew Knowles and Sons was a coal mining company that operated on the Manchester Coalfield in and around Clifton, in the historic county of Lancashire, England.
Byrom, Allen, Sedgwick and PlaceThe first bank in Manchester, founded in 1771. It collapsed in 1788 when one of its major borrowers declared bankruptcy.
Winter HillThe high point of Rivington Moor in the West Pennine Moors is 1,496 feet high and has been the site of mining, a mass trespass, aeroplane disasters and murder.
RHS Garden BridgewaterThe Royal Horticultural Society's first new garden since 2003, opening in 2020 in Worsley, in the City of Salford.
Worsley New HallWorsley's third manor house, New Hall was built in 1846 to designs by Edward Blore for Francis Egerton, 1st Earl of Ellesmere.
Ellesmere CollieryEllesmere Colliery in Walkden, on the Lancashire Coalfield, was sunk in 1865 by the Bridgewater Trustees. Production ended in 1923.
Worsley Navigable LevelsExtensive network of underground canals that drained the Duke of Bridgewater's coal pits emerge into the open at the Delph in Worsley, Greater Manchester.
1996 Manchester bombingAttack carried out by the Provisional Irish Republican Army on Saturday 15 June 1996, when they detonated a 15,000 kg bomb in the centre of Manchester, England.
Imperial War Museum NorthMuseum in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford in Greater Manchester, England. One of five branches of the Imperial War Museum, it explores the impact of modern conflicts on people and society.
Boggart Hole CloughLarge woodland area and country park in Greater Manchester, what remains of an ancient woodland.
Chaddock PitPit sunk in about 1820 by the Bridgewater Trustees that was connected to the Bridgewater Canal at Boothstown Basin by an underground canal.
CottonopolisThe nickname given to Manchester, the world's first industrial city, a metropolis centred on cotton trading.
Bridgewater CollieriesCoal mining company on the Lancashire Coalfield with headquarters in Walkden near Manchester.
Trafford Ecology ParkDesignated Site of Biological Importance and Local Nature Reserve in Trafford, Greater Manchester.
Red MossWetland moss and local nature reserve between Horwich and the M61 motorway in Greater Manchester.
Worsley dry docksEarliest surviving example of a dry dock on Britain's canals.
Standedge crossingsStandedge has been a major Pennine crossing point for more than 2,000 years.
St George’s Church, TyldesleyWaterloo church dedicated to St George, completed in 1825 to serve the growing township of Tyldesley cum Shakerley.
St John’s Church, Mosley CommonActive church in Mosley Common that was built in 1886.
St Mary the Virgin’s Church, LeighAncient parish church that served six townships.
St Stephen’s Church, AstleyParish church in Astley, Greater Manchester, built in 1968 after its predecessor was destroyed by arson.
Chowbent ChapelActive Unitarian place of worship in Atherton, Greater Manchester that was built in 1721.
St John the Baptist’s Church, AthertonAnglican parish Church in Atherton, Greater Manchester designed by Paley and Austin and completed in 1896
St Mark’s Church, WorsleyActive Anglican parish church in Worsley, Greater Manchester with an unusual thirteen-striking clock.
DiggleOne of several villages in the Saddleworth parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham, in Greater Manchester
Howe BridgeSuburb of Atherton in Greater Manchester, built as a model mining village in the 1870s by the Fletchers.
SaddleworthCivil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham in Greater Manchester, in Yorkshire until government reorganisation in 1974.
Salford QuaysArea of Salford, Greater Manchester, England at the terminus of the Manchester Ship Canal. Previously the site of Manchester Docks, also known as Salford Docks, it became one of the first and largest urban regeneration projects in the United Kingdom following the closure of the dockyards in 1982.
Manchester DocksRedirected to Salford Quays.
Salford DocksRedirected to Salford Quays.
New ManchesterFormerly isolated mining community at the extreme eastern end of the Tyldesley township.
Manchester BankRedirected to Byrom, Allen, Sedgwick and Place.
St Mary the Virgin’s Church, EllenbrookActive Anglican church of ancient foundation.
EllenbrookResidential suburb of Worsley in the City of Salford in Greater Manchester, England.
Ellenbrook ChapelRedirected to St Mary the Virgin's Church, Ellenbrook.
Ellenbrook tramwayA tramway built by the Bridgewater Trustees in the 1830s to transport coal to the Bridgewater Canal.
Lever Park, RivingtonGrade II listed country park between Rivington in Lancashire and Horwich in Greater Manchester.
Jonathan SimpsonArchitect who was born, educated and practised in Bolton.
Stretford Town HallRedirected to Trafford Town Hall.
Pilkington’s Lancastrian Pottery & TilesFormer manufacturer of tiles, vases and bowls established in 1892, best remembered for their fine glazes such as Royal Lancastrian.
White City, StretfordFormer botanical gardens that hosted the largest art exhibition ever held in the UK, now a retail park.
Bedford CollieryColliery in Leigh sunk by John Speakman at Wood End Farm in the northeast part of Bedford in 1875
Dicky BeefsRedirected to New Hall moat.
Chanters CollieryFormer colliery in Hindsford, Atherton where coal was mined from 1854 until 1966.
StretfordOne of the four major urban areas in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford, Greater Manchester.
Stretford Civic TheatreRedirected to Stretford Public Hall.
St Martin’s Church, Ashton upon MerseyGrade II* listed church in Sale, Greater Manchester.
Eyebrow Cottage, SaleOldest surviving building in Sale, Greater Manchester, built c.1670.
Walkden GardensPublic green space in Sale, Greater Manchester.
All Saints’ Church, UrmstonGrade I listed Roman Catholic Church in Urmston, Greater Manchester.
Manchester MuseumLargest university museum in the UK, founded in 1867.
Flixton HouseGrade II listed building in Flixton, Greater Manchester, scene of the Flixton Footpath Battle of 1826.
Cotterill Clough Nature ReserveNature reserve adjacent to Manchester Airport.
Royd HouseDesigned by the architect Edgar Wood, and considered to be one of the most advanced examples of early 20th-century domestic architecture.
Skyhooks (Trafford Park)Pair of 18-metre high statues at the northern entrance to Trafford Park, erected in 1995 to mark the area's regeneration
TyldesleyFormer industrial town in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan, in Greater Manchester.
AstleyVillage in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan, formerly a coal-mining area, but now part of a commuter belt for the nearby city of Manchester.
ShakerleySuburb of Tyldesley in Greater Manchester, anciently a hamlet in the northwest of the township.
Mosley CommonSuburb of Tyldesley in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan, in Greater Manchester.
Sacred Heart Church, HindsfordRedundant Catholic church originally intended to serve the families of Irish Catholic immigrants.
St Joseph’s Roman Catholic Church, LeighActive Roman Catholic church in Bedford, Leigh in Greater Manchester, a designated Grade II listed building.
Tyldesley Top ChapelThe township of Tyldesley's first place of worship, built in 1789.
Bedford, LeighSuburb of Leigh in Greater Manchester, one of the three ancient townships that merged in 1875 to form the town of Leigh.
Bedford HallLate-medieval house in Bedford, Leigh near the edge of Chat Moss.
St Paul’s Church, PeelActive Anglican parish church in Little Hulton, Greater Manchester, built between 1874 and 1876.
Liverpool Road railway station warehouseGrade I listed warehouse, part of the Liverpool Road railway station complex.
St Lawrence, DentonGrade II* listed church in Denton, Greater Manchester, one of only 29 surviving timber-framed churches in England.
St Ann’s, StretfordActive Roman Catholic church in Stretford, Greater Manchester, a designated Grade II listed building completed in 1867.
St Matthew’s, StretfordActive Anglican church in Stretford, Greater Manchester, built in 1841–1842.
St Anne’s, DentonActive Anglican church in Denton, Greater Manchester, a designated Grade I listed building completed in 1882.
Grade I listed buildings in BoltonGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Bolton, in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in BuryGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Bury, in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in ManchesterGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Manchester, in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in RochdaleGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale, in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in SalfordGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Salford, in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in StockportGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Stockport, in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in TamesideGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Tameside in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in TraffordGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in WiganGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan in Greater Manchester.
Grade I listed buildings in WiganGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan Borough of Wigan in Greater Manchester.
Manchester Art MuseumEducational venture undertaken by the philanthropist Thomas Horsfall, inaugurated in 1877. It closed in 1953, and most of its collection is now in the possession of the Manchester Art Gallery.
Union Baptist Church, StretfordGrade II listed former Union Baptist Church in Stretford, Greater Manchester, opened in 1867 and owned by the Iglesia ni Cristo since 2012.
Mayfield Park, ManchesterFirst public park built in the city of Manchester for more than a century, officially opened in 2022.
Southern Cemetery, ManchesterLargest municipal cemetery in the United Kingdom, opened in 1879.
St Antony of PaduaTin tabernacle in the Trafford Park industrial estate in Manchester.
Nob EndLocal Nature Reserve (LNR) and biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) near Bolton, Greater Manchester.
St Werburgh’s Church, WarburtonName given to two separate Anglican churches in the village of Warburton, Greater Manchester.
Great Woolden HallRedirected to Irlam, Great Woolden Hall.
Cadishead ViaductDisused railway viaduct over the Manchester Ship Canal, built in 1893.
Outwood ViaductGrade II listed railway viaduct crossing the River Irwell in Radcliffe, Greater Manchester.
Blackfriars Bridge, ManchesterGrade II listed bridge connecting Salford to Manchester across the River Irwell.
Prestolee AqueductGrade II listed aqueduct in Prestolee, Kearsley, Greater Manchester, crossing the River Irwell on the Manchester, Bolton and Bury Canal.
Clifton AqueductGrade II listed aqueduct in Clifton, Greater Manchester, crossing the River Irwell on the Manchester, Bolton and Bury Canal.
Manchester Reform ClubGrade II* listed former gentleman's club, completed in 1871.
Manchester ClubRedirected to Manchester Reform Club.
Grade I listed buildings in Greater ManchesterGrade I listed buildings in the Metropolitan County of Greater Manchester, split into its constituent metropolitan boroughs.